Search Knowledge Base by Keyword
What are CNAME records?
CNAME records or Canonical Name records function as aliases for domain names of another canonical domain name. This is generally suitable to point domains with a subfolder to a subdomain within a single primary domain name.
An example of its working is shown below with the URL:
https://www.ukhost4u.com/billing/
When this site resolves, it is seen that it is exactly similar to the domain:
CNAME must always point to a domain and never to an IP address. This concept can be explained with the below example.
Suppose we have two wesbites with the name “example.com” and “www.example.com” and both these websites point to the same application and are hosted on the same server
So here, A record will be “example.com” which point outs to its IP address, and “CNAME” will be “www.example.com” which will be pointing to “example.com”
As a result, “example.com” points out to the IP Address while “www.example.com” point out to “example.com” which in turn point out to the same IP Address
NOTE – A CNAME should always point out to some other domain name which in turn points out to IP Address.
DNS Editor will always highlight the error if the user tries to map IP Address with the CNAME
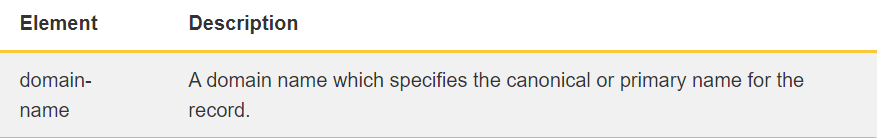
CNAME Format –
CNAME record follows the below format –
Restriction On Using CNAME records-
CNAME cannot be pointed to MX and NS records. They have to point to an A record first before mapping to a CNAME record. An MX record is also known as the mail exchange record and an NS record is a name server record and denotes which DNS record is authorized to access the server.
